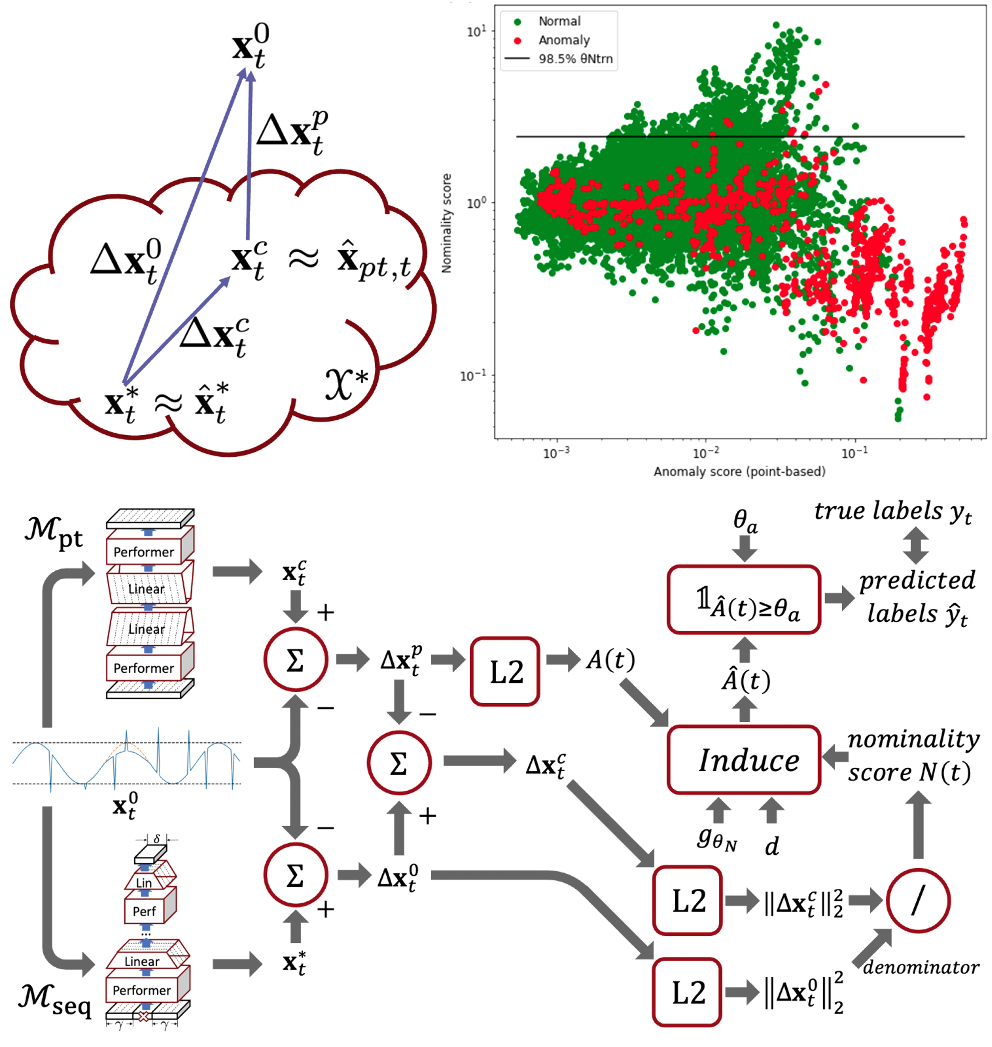
Time series anomaly detection is challenging due to the complexity and variety of patterns that can occur. One major difficulty arises from modeling time-dependent relationships to find contextual anomalies while maintaining detection accuracy for point anomalies. In this paper, we propose a framework for unsupervised time series anomaly detection that utilizes point-based and sequence-based reconstruction models. The point-based model attempts to quantify point anomalies, and the sequence-based model attempts to quantify both point and contextual anomalies. Under the formulation that the observed time point is a two-stage deviated value from a nominal time point, we introduce a nominality score calculated from the ratio of a combined value of the reconstruction errors. We derive an induced anomaly score by further integrating the nominality score and anomaly score, then theoretically prove the superiority of the induced anomaly score over the original anomaly score under certain conditions. Extensive studies conducted on several public datasets show that the proposed framework outperforms most state-of-the-art baselines for time series anomaly detection.
We coin our method Nominality score conditioned time series anomaly detection by Point/Sequential Reconstruction (NPSR).
Related Publications
- C.-Y. Lai, F.-K. Sun, Z. Gao, J. H. Lang, D. S. Boning, Nominality Score Conditioned Time Series Anomaly Detection by Point/Sequential Reconstruction, Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023.
[arXiv] [NeurIPS] [GitHub] - C.-Y. Lai, F.-K. Sun, J. H. Lang, D. S. Boning, Unsupervised Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection for High-Frequency Data, Microsystems Annual Research Conference (MARC), (2023).
[proceedings]